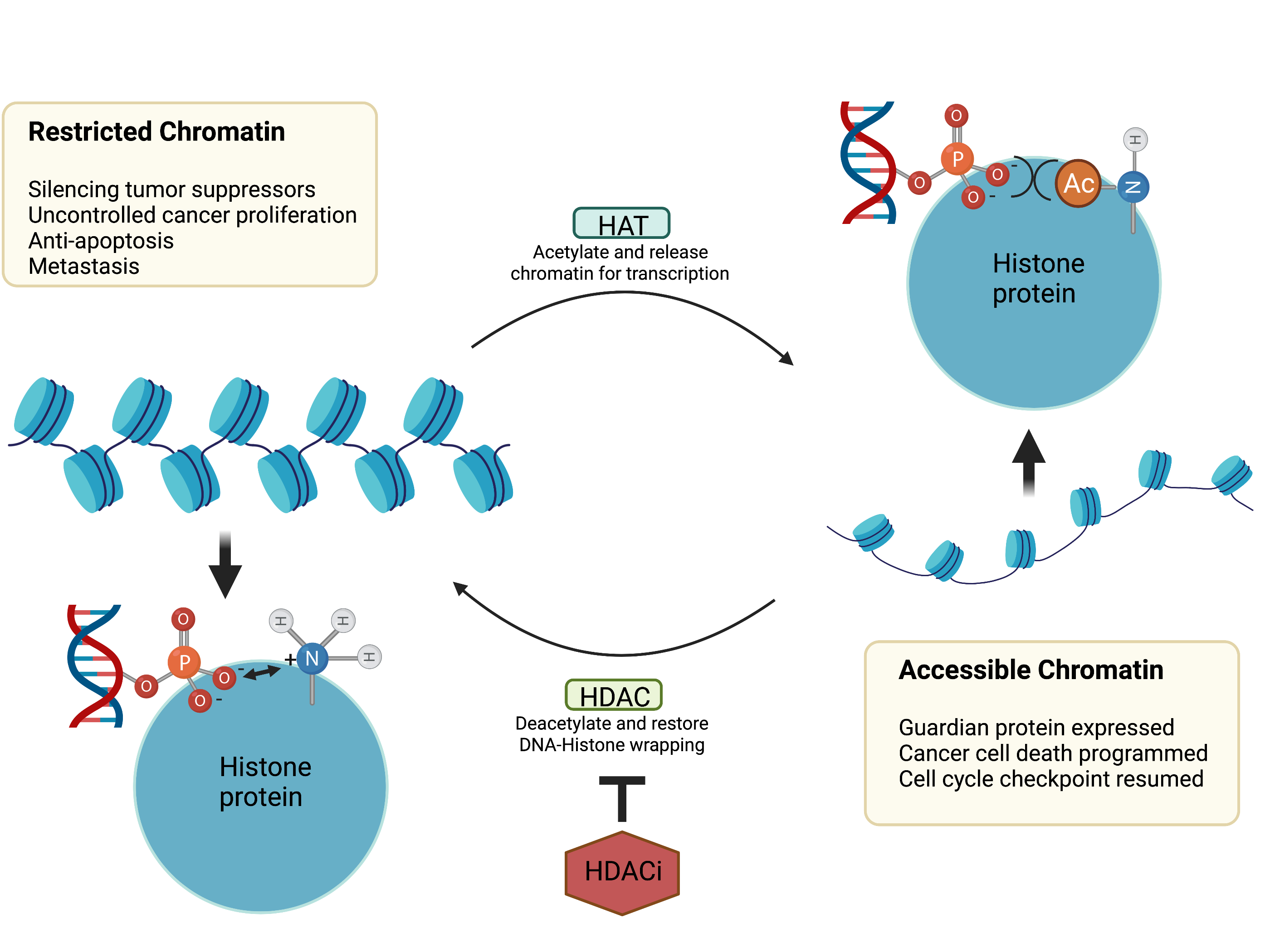
COX are a family of proteins that induce tissue inflammations. COX1 is known as a constituitive protein in the human body and an essential cytokine for protecting GI system, which COX-2 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine which induce tissue inflammation, necrosis and carcinogenesis. The COX-2 inhibitors have been regarded as analgesic drugs, anti-inflammation drugs, and potential anti-cancer agents. However, recent research found that COX-1 also regulates some types of cancers such as the Ovarian cancer. Thus, COX inhibitors in cancer research is highly interested and more studies are needed.
A simple graphic information for COX pathway and LOX pathway in the Arachidonic acid regulation.
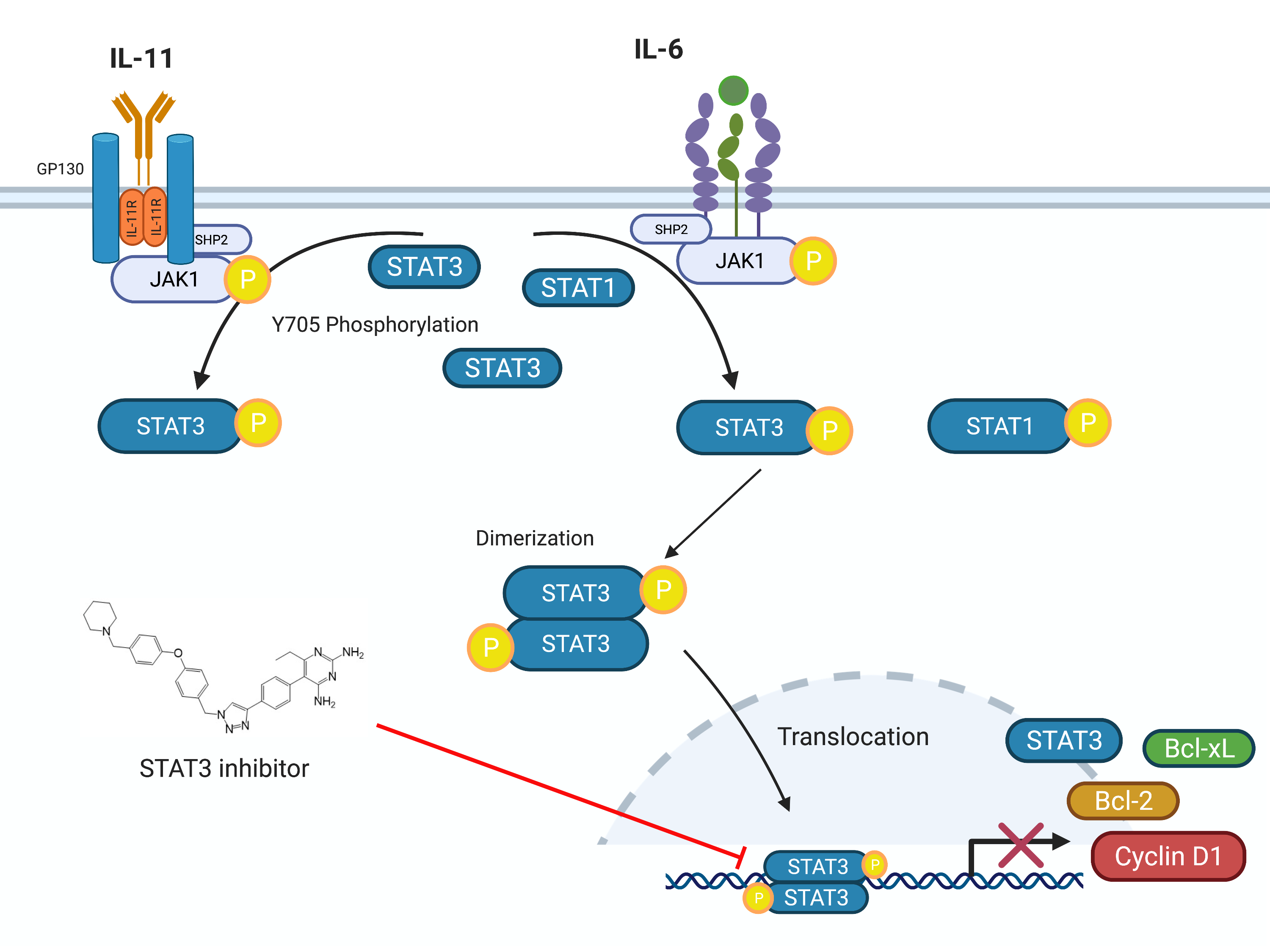
Establishing structure–activity relationships (SAR) for privileged pharmacophores, such as the indole scaffold, is a key step in the early stages of drug discovery. Herein, we report the synthesis and preliminary SAR studies on substituted 6-hydroxyindole-7-carboxylates as a tunable framework for COX inhibition and anti-cancer activity. To facilitate the SAR discovery, a modular synthetic methodology was employed which enabled the synthesis of the substituted indoles. From the synthesized compounds, five displayed COX-1 inhibition activity in a colorimetric assay with their intracellular activity further confirmed by a cell-based target validation assay. Following molecular docking analyses, key interactions between the active compounds and the COX enzymes were elucidated. In addition to the identified COX inhibitors, two compounds showed selective cytotoxicity against Hep-G2, MCF-7, and LnCaP. The mechanism of cell death was investigated and found to include induction of Caspase-3 activation and cleavage, down-regulation of anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-xL and Bcl-2, and upregulation of Bax. Finally, two representative compounds were confirmed to induce cell cycle arrest at the G1/G0 stage. In summary, the 6-hydroxyindole-7-carboxylate framework shows promising versatility as a template for the discovery of anti-inflammation or anti-cancer agents, given the evidence of its COX inhibitory and anti-cancer activities herein presented.